Parasitic Nutrition In Protozoa
The free-living members of the family are found in surroundings containing little or no free oxygen. And 4 all of the Sporozoa exhibit parasitic nu-trition.

Nutrition In Protozoa Navodita George Maurice Academia Edu
The life cycle of parasitic protozoa occurs intracellular or in the lumen of given organs.
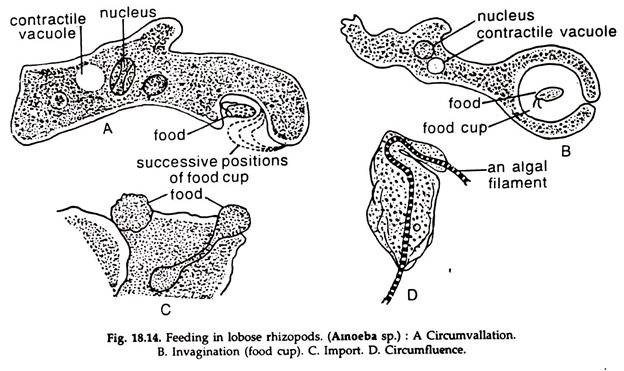
Parasitic nutrition in protozoa. This is often mediated by specialized transporter proteins that ensure the nutritional requirements of the parasite are met. Parasites inhabiting the intestine and blood have a distinct mouth through which food particles are ingested through the process of phagotrophy. Parasites like protozoa live almost everywhere and can easily get inside us in many different ways.
Free-living aquatic freshwater seawater and parasitic ectoparasites or endoparasitesThey are also commensal in habitat. There are about 50000 known species of Phylum Protozoa. They are the simplest and.
They have heterotrophic mode of nutrition whereby the free-living forms ingest particulates such as bacteria yeast and algae while the parasitic forms derive nutrients from the body fluids of their hosts. They have flagella for locomotion. Protozoa Classification and Examples.
Nutrition of parasitic protozoa. Holozoic or Zoo-Trophic Nutrition 2. The Protozoa are considered to be a subkingdom of the kingdom Protista although in the classical system they were placed in the kingdom Animalia.
The Bodonidae are free living protozoa or parasites of lower animals without economic importance. In some protozoa other terms are used for these stages. On the other hand the microbiota composition can affect the survival physiology and virulence of many parasitic protozoa.
The following points highlight the seven important modes of nutrition in Protozoa. Protozoa is a phylum having unicellular heterotrophs. More than 50000 species have been described most of which.
Cysts are stages with a protective membrane or thickened wall. Our knowledge however of the metabolism of representative Protozoa remains fragmentary. Protozoans exhibit mainly two forms of life.
Mastigophora or Flagellated protozoans. The following points highlight the top four modes of nutrition in protozoa. Holophytic Holos Whole Phyton Plant Origin or Autotrophic Photosynthesis 3.
Parasitic protozoa such as malaria parasites trypanosomes and Leishmania acquire a plethora of nutrients from their hosts employing transport proteins located in the plasma membrane of the parasite. Based on the kinds of food nutrients taken in 2 class of protozoa 1 Phagothropic if protozoa takes in large particles of food 2 Saprozoic Obtaining nourishment by absorption of dissolved organic and inorganic materials The manner of nutrition in Protozoa varies depending on species and where it lives. The osmotrophic forms of protozoa are either coelozoic or.
The very specialized nutrients required by parasitic forms have demonstrated interesting evolutionary relationships. Protozoa are classified into three main category based on their mode of nutrition such as. The loss of key biosynthetic pathways is a common feature of important parasitic protists making them heavily dependent on scavenging nutrients from their hosts.
They make up about 1 of angiosperms and are found in almost every biomeAll parasitic plants have modified roots called haustoria which penetrate the host plant connecting them to the conductive system either the xylem the phloem or both. The mechanisms used by parasitic protozoa are almost are similar to that of their non-parasitic protozoa. Nutrition of parasites Mechanism of food getting same in parasitic non-parasitic forms Zoomastiogophora Trichomonas has a cytostome for food ingestion by phagotrophy Many parasitic ciliates.
They reproduce primarily by asexual means although in some groups sexual modes also occur. An increasing number of biochemical experiments is being reported on the existence of various enzyme systems in the Protozoa. The accessory growth-factor requirements of these forms are complex.
Parasitic forms all of the Ciliata utilize solid food. About 26 species of protozoa are identified to be parasitic to humans. The very specialized nutrients required by parasitic forms have demonstrated interesting evolutionary relationships.
Some of the characteristics are. All parasitic protozoa require preformed organic substancesthat is nutrition is holozoic as in higher animals. However many parasitic protozoa like Entamoeba practice holozoic nutrition.
They are liable for producing dreadful diseases like Sleeping sickness Malaria and many others. These eukaryotic pathogens have evolved with the vertebrate immune system and typically produce long-lasting chronic. Many protozoa live inside the body of other living organism and nourish themselves from the food of the host.
Classification of Protozoa based on the Mode of Nutrition. Autotrophic or Holophytic Nutrition 4. In some cases the digested or decomposed substances of the hosts enter into the body of the parasites by diffusion as in Monocystis.
All parasitic protozoa require preformed organic substancesthat is nutrition is holozoic as in higher animals. A lot of absolutely free living Protozoans feed on the faecal subject of other animals and are termed as coprozoic. Myxotrophic nutrition Combination of more than 1- mode of nutrition Many protozoa use photosynthesis or osmotrophy or phagotrophy Euglena Peranema fF.
Resistance to parasitic protozoa appears to be similar to resistance against other infectious agents although the mechanisms of resistance in protozoan infections are not yet as well understood. Explanation of possible interactions between the microbiota immune. Application of molecular genetic approaches and the completion of genome projects have allowed t.
They are parasites or free-living. It comes under Kingdom Protista. The stages of parasitic protozoa that actively feed and multiply are frequently called trophozoites.
Most of the colorless free-living proto-zoans exhibit wholly or in part holozoic nutrition. Protozoa are divided into four major groups based on the structure and the part involved in the locomotion. Resistance can be divided into two main groups of mechanisms.
In this discussion a rather brief consideration of our knowledge of holophytic and saprophytic nutrition in the Protozoa is followed by a. Some of these ways include. In contrast protozoa will usually obtain their nutrition by engulfing swallowing up andor enclosing food particles and small nutrient particles such as bacteria algae or even other protozoa.
Saprophytic Sapros Rotten or Saprozoic 4. Because of the diversity different species follow different patterns of life cycle. Parasitic protozoa are a major cause of global infectious disease.
1 nonspecific mechanisms or factors such as the presence of a nonspecific serum component that is. A parasitic plant is a plant that derives some or all of its nutritional requirement from another living plant. They are small usually microscopic not visualize without a microscope.
The publication takes a look at the nutrition of parasitic amebae biochemistry of Plasmodium and the influence of antimalarials and the.

Protozoa Examples Characteristics Types What Is Protozoa Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
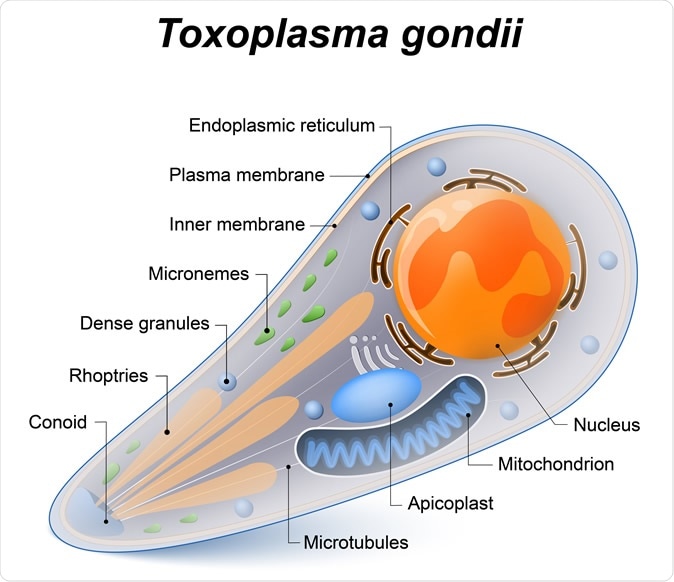
Dangerous Brain Parasite Invades Host Cell Maintains Steady Nutrient Supply

Protozoa Nutrition Respiration And Excretion

Unicellular Eukaryotes Ppt Video Online Download

Phylum Protozoa Nutrition And Parasitism Study Score

Phylum Protozoa Nutrition And Parasitism Study Score

Nutrition In Protozoa 4 Modes Zoology

Phylum Protozoa Nutrition And Parasitism Study Score

Post a Comment for "Parasitic Nutrition In Protozoa"