Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Disease Controversy Unresolved
It is also linked with worse cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Vitamin D deficiency is a prevalent global problem caused mainly by low exposure to sunlight.

Vitamin D Calcium Supplements And Implications For Cardiovascular Health Jacc Focus Seminar Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology
Photosynthesis Dietary Intake and Metabolism of Vitamin D.

Vitamin d and cardiovascular disease controversy unresolved. 101016jjacc201705031 Crossref Medline Google Scholar. Causality J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. If we consider the amount of vitamin D per 100 g of weight the best sources of vitamin D are represented by cod liver oil 90250 mcg fatty fish like.
Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. Vitamin D has long been known to be an essential part of bone metabolism although recent evidence suggests that vitamin D plays a key role in the pathophysiology of other diseases including CVD as well. Among the potentially relevant mechanisms for cardiovascular diseases vitamin D may influence blood pressure through the renin-angiotensin system parathyroid hormone levels myocardial function inflammation and vascular calcification.
Vitamin D deficiency is widespread the lowest vitamin D levels are commonly found in regions such as the Middle East and South Asia and the main risk factors were attributed to elderly women higher latitude winter season less sunlight exposure skin pigmentation dietary intake and low vitamin D fortified foods It was estimated that the. However meta-analyses of vitamin D supplementation trials have failed to show clear improvements in blood pressure insulin sensitivity or lipid parameters thus suggesting that the link between vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular disease may be an epiphenomenon. Vitamin D deficiency as well as cardiovascular diseases CVD and related risk factors are highly prevalent worldwide and frequently co-occur.
13-16 Owing to insufficient data regarding cardiovascular benefits of screening and. Vitamin D 3 and 25OHD 3 are found in fish eggs meat and dairy products. J Am Coll Cardiol.
There is controversy about the definition of vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D the optimum serum level of 25OHD and the dietary requirements of vitamin D. Vitamin D and cardiovascular risk. Nat Rev Cardiol 13 2016 pp.
It is also linked with worse cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Observational studies have suggested an inverse association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and risk of cardiovascular disease CVD events. Is a matter of controversy.
Thus we aimed to identify the associations of the longitudinal trajectory of vitamin D status with. But recent studies found vitamin D supplements did not bolster heart health. 123 Specifically low vitamin D levels have been linked to an increased risk of myocardial infarction MI stroke CVD mortality and heart failure in case-control and other prospective.
23 A British trial that tested 100 000 IU of vitamin D 3 or placebo every 4 months equivalent to 833 IUd for up to 5 years with cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular risk appears especially elevated at 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels below 10 or 15 ngmL and. Biologically plausible mechanisms have been proposed to link vitamin D to coronary heart disease CHD prevention and observational studies suggest an inverse association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D 25OHD concentrations and CHD.
Supplementation with vitamin D has received attention as a potential cardioprotective strategy. Lowered vitamin D level has been reported to be one of risk factors for coronary heart disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 10 chronic kidney disease 11 and human immunodeficiency. Article Download PDF View Record in Scopus Google Scholar.
Although vitamin D is best known for its role in developing strong bones low blood levels have been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. Al Mheid I Quyyumi AA. Background and ObjectivesVitamin D has been indicated to play an important role in the optimal function of the cardiovascular system.
Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease prevention. 78 The Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline defines vitamin D deficiency as 25OHD level. Initially there was a lot of enthusiasm for vitamin D treatment for cardiovascular disease and this was.
1112 Assessment of vitamin D supplementation for cardiovascular disease prevention has been a subject of growing interest in recent randomized clinical trials RCTs. However vitamin D receptors are found in most human cells and tissues indicating many extra-skeletal effects of the vitamin particularly in the immune. A prospective randomized controlled trial of the effects of vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular.
Vitamin D regulates blood pressure cardiac functions and endothelial and smooth muscle cell functions thus playing an important role in cardiovascular health. However with limited evidence it remains unclear whether vitamin D status transition during childhood would affect cardiometabolic risk factors. Google Scholar Avolio A Avataneo V Manca A.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Excess. J Am Coll Cardiol 70 2017 pp. As expected 2829 VitD and PTH inversely correlate No effect of aging was observed on VitD data not shown whereas PTH increases along groups of age R 2 0061 P 0001The relationship between VitD and PTH though remains significant at each age group 2040 4060 and 6080 years Fig.
2No effects of age on the relationship. The main role of 125 dihydroxyvitamin D is the maintenance of calcium and phosphorus homeostasis. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2.
J Am Coll Cardiol. Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Disease. Vitamin D consists of a group of fat-soluble molecules called secosteroids which are similar to steroids but with broken rings and that exist in several forms Its designation as a vitamin is a misnomer given that human skin synthesizes cholecalciferol or vitamin D 3 by the photochemical cleavage of cutaneous 7.
Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease. PMC free article Google Scholar. Gepner AD Ramamurthy R Krueger DC Korcarz CE Binkley N Stein JH.
There is a paucity of randomized controlled trials of vitamin D and cardiovascular disease events and absence of any trials with cardiovascular disease as the primary prespecified outcome. However meta-analyses of vitamin D supplementation trials have failed to show clear improvements in blood pressure insulin sensitivity or lipid parameters thus suggesting that the link between vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular disease may be an epiphenomenon. Vitamin D level supplementation has increased in primary care settings in the United States.
Vitamin D and cardiovascular diseases.

Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Health Clinical Nutrition

Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Disease Controversy Unresolved Sciencedirect
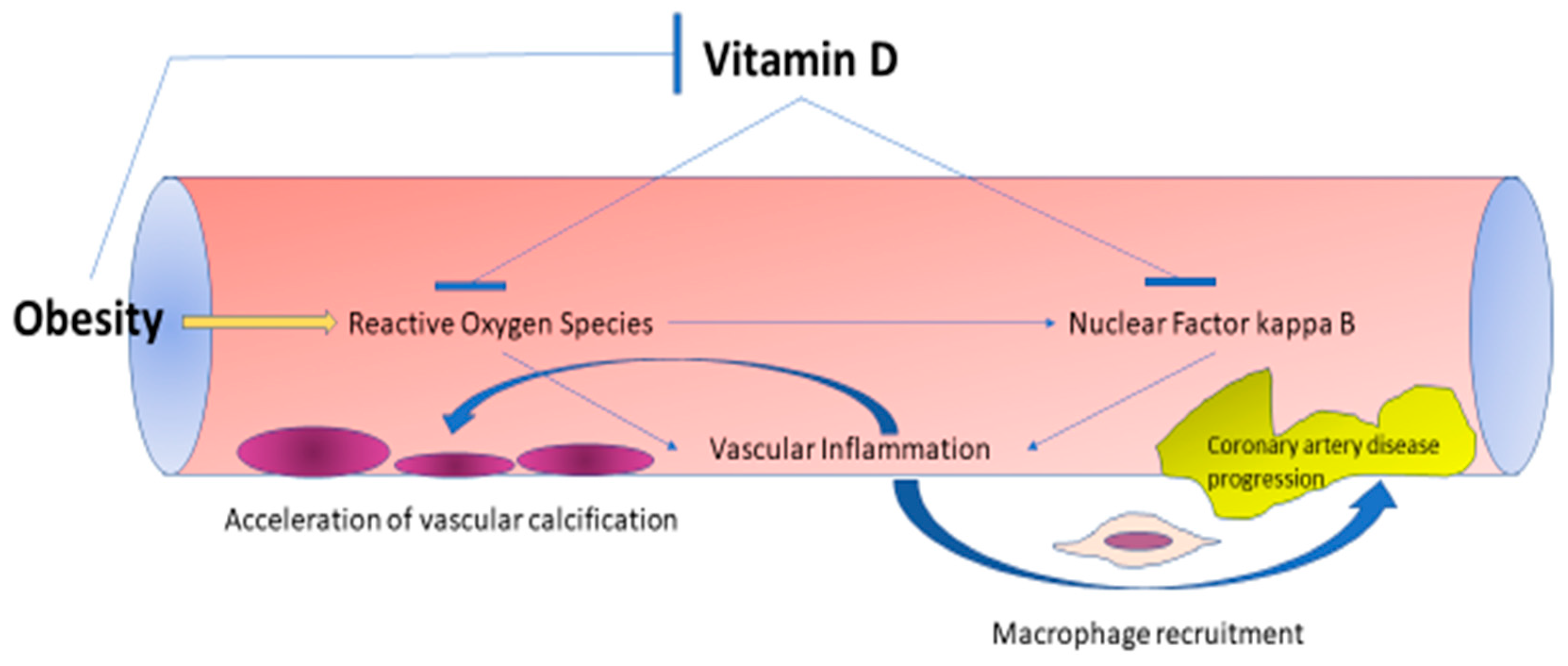
Nutrients Free Full Text The Impact Of Obesity On The Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency And Cardiovascular Disease Html

Figure 2 From Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Disease Is The Evidence Solid Semantic Scholar

Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Health Clinical Nutrition
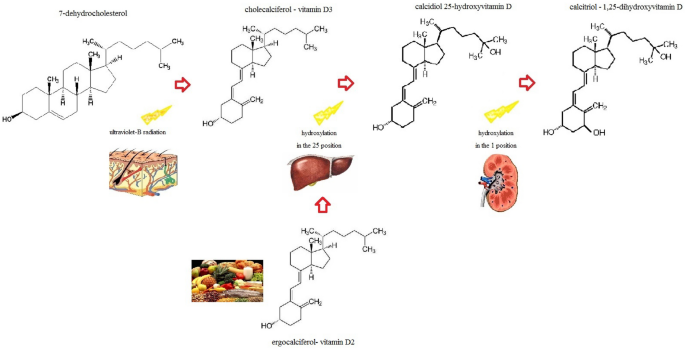
Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Disease Risk A Literature Overview Springerlink

Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Health Clinical Nutrition

Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Disease Where Do We Stand In 2017
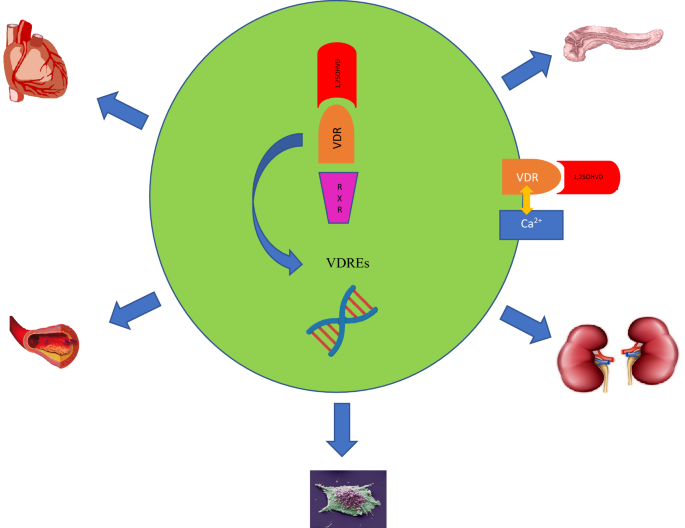
Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Disease Risk A Literature Overview Springerlink
Post a Comment for "Vitamin D And Cardiovascular Disease Controversy Unresolved"