Review Article Vitamin D And Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Epidemiologic data have associated vitamin D deficiency with an increased risk of IBD hospitalizations surgery and loss of response to biologic therapy. In recent years the immunomodulating effects of vitamin D have gained a huge interest in its possible pathogenic influence on the pathophysiology of IBD.

Potential Therapeutic Effect Of Vitamin D In Ibd Hrqol Health Related Download Scientific Diagram
Management of inflammatory bowel disease IBD including ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease is generally cumbersome for patients and is a massive health-economic burden.

Review article vitamin d and inflammatory bowel diseases. Evidence concerning the therapeutic role of vitamin Dsynthetic vitamin D receptor agonists in clinical and experimental models of in ammatory bowel disease far beyond the role of calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism. Both local as well. The commonly quoted definition of vitamin D deficiency is a 25OHD level less than 25 nmolL 10 ngmL the level that places an individual at highest risk for development of osteomalacia.
Recent evidence supports a central role of this micronutrient in the course of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases IBD. In this article we review recent. Initially this finding was correlated with metabolic bone disease.
Inflammatory bowel disease IBD is characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract but it is difficult to define because it is a complex set of debilitating disorders where physiology microbiology immunology and genetics are all disrupted. 203 However the Endocrine Society has recently published a less conservative level of less than 50 nmolL 20 ngmL as vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin whose active form calcitriol or 125-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 125OH 2 D 3 regulates bone calcium and phosphorus metabolism However vitamin D also influences immune system function and deficiency has been recognized as an environmental risk factor for autoimmune diseases like Crohns disease CD.
Vitamin D deficiency has been recognized as an environmental risk factor for Crohns disease since the early 80s. This conceptual expansion has been underpinned by identification and exploration of components of this axis including vitamin D. Subsequently low serum vitamin D levels have been reported in various immune-related diseases pointing to an immunoregulatory role.
The key underlying pathogenic mechanisms for both diseases is a dysregulated host immune response to commensal intestinal flora in genetically susceptible individuals 1 2Known genetic variants incompletely explain the variance in. The immunological effects of vitamin D have increasingly come into focusTo review the evidence supporting a role of vitamin D in inflammatory bowel diseasesA comprehensive search was performed on PubMed using the terms crohns disease ulcerative colitis and vitamin DVitamin D deficiency is. Vitamin D is traditionally associated with bone metabolism.
Review World Journal of Gastroenterology 103748wjgv22i31045 22 3 1045 2016. Vitamin D is an immunoregulatory factor influencing intestinal homeostasis. To review the evidence supporting a role of vitamin D in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Indeed vitamin D and its receptor VDR. Ulcerative colitis UC and Crohns disease CD constitute chronic idiopathic inflammatory bowel diseases IBD. Understanding of the role of vitamin D in health and disease has increased markedly in the past decade with its involvement extending well beyond traditional roles in calcium and phosphate homeostasis and musculoskeletal health.
Vitamin D deficiency causes more severe growth retardation and weight loss and also led to higher mortality in IL-10 KO mice colitis. As a chronic disease IBD mainly includes ulcerative colitis UC and Crohns disease CD. 4 Vitamin D.
Ulcerative colitis UC and Crohns disease CD constitute chronic idiopathic inflammatory bowel diseases IBD. This narrative review aims to provide a general overview of the possible biological mechanisms of action of vitamin D and its therapeutic implications in. Absorption of vitamin D in patients with CD even in those with quiescent disease29 Protein-losing enteropa-thy occurs in some patients with IBD.
72 Disease severity correlated with vitamin D status in mice with DSS-induced colitis. As a result it is well established that vitamin D supplementation in this population is important. In tune with its immune-modulating effects vitamin D may also influence severity of inflammation in IBD.
Moreover chronic inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular disease asthma inflammatory bowel disease chronic kidney disease nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and others tend to have lower vitamin D status which may play a pleiotropic role in the pathogenesis of the diseases. Vitamin D and inflammatory bowel diseases. As vitamin D and its metabolites circulate predominantly as bound forms Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014.
Inflammatory bowel disease IBD comprising Crohns disease CD and ulcerative colitis UC is a group of. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels have been repeatedly reported in inflammatory bowel diseases together with a relationship between vitamin D status and disease activity. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels have been repeatedly reported in inflammatory bowel diseases together with a relationship between vitamin D status and.
Summary Background Understanding of the role of vitamin D in health and disease has increased markedly in the past decade. Andrzej Wędrychowicz Advances in nutritional therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Abreu MT et al.
Introduction Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin whose active form cal-citriolor -dihydroxyvitaminD 3 OH 2 D 3regulates. This study explored the association between serum vitamin D levels and inflammatory bowel disease in a Chinese populationSixty-five patients with ulcerative colitis UC and 50 with Crohns. Vitamin D is a secosteroid hormone that possesses immunomodulatory properties and has been demonstrated to potentially influence inflammatory bowel disease IBD pathogenesis and activity.
Vitamin D and inflammatory bowel disease established concepts and future directions. 2004 Measurement of vitamin D levels in inflammatory bowel disease patients reveals a subset of Crohns disease patients with elevated 125-dihydroxyvitamin D and low bone. Patients with IBD are at risk of low bone density and increased fractures due to low vitamin D levels long standing disease and frequent steroid exposures.
Vitamin D deficiency is commonly diagnosed among patients with inflammatory bowel disease IBD. Inflammatory bowel diseases IBDs including ulcerative colitis UC and Crohns disease CD are idiopathic intestinal disorders that are characterized by repetitive episodes of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract usually associated with bloody diarrhea tenesmus and abdominal pain while the location of the disease and the thickness of the. 125-136 127 ª 2013 John Wiley Sons Ltd Review.
The key underlying pathogenic mechanisms for both diseases is a dysregulated host immune response to commensal intestinal flora in genetically susceptible individuals 1 2Known genetic variants incompletely explain the.

Vitamin D Sources Metabolism And Effects On Immune System Download Scientific Diagram

Summary Of Causes Of Vitamin D Deficiency And Diseases And Disorders Download Scientific Diagram

Vitamin D Sources Metabolism And Effects On Immune System Download Scientific Diagram

Potential Therapeutic Effect Of Vitamin D In Ibd Hrqol Health Related Download Scientific Diagram
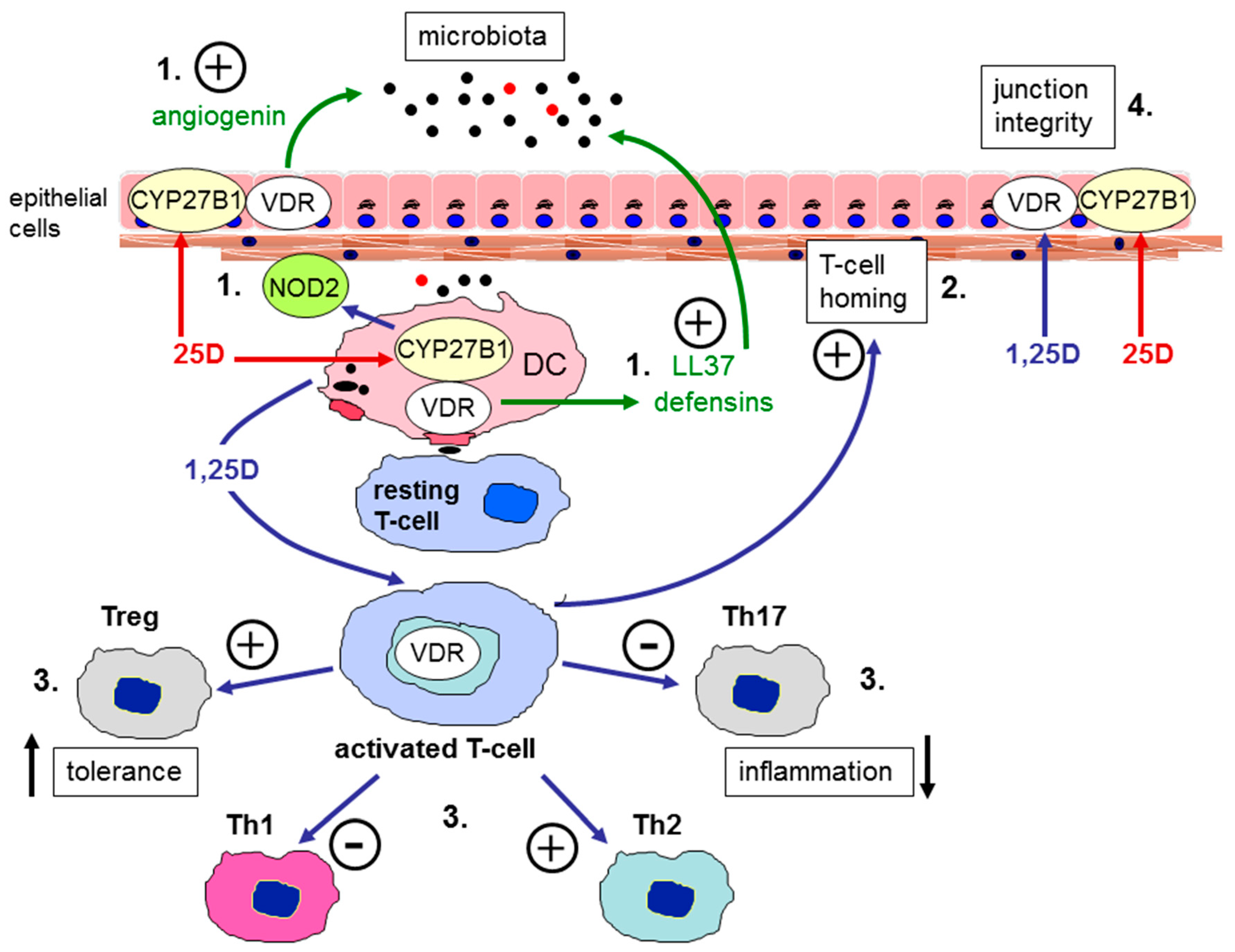
Nutrients Free Full Text The Role Of Vitamin D In Inflammatory Bowel Disease Mechanism To Management Html
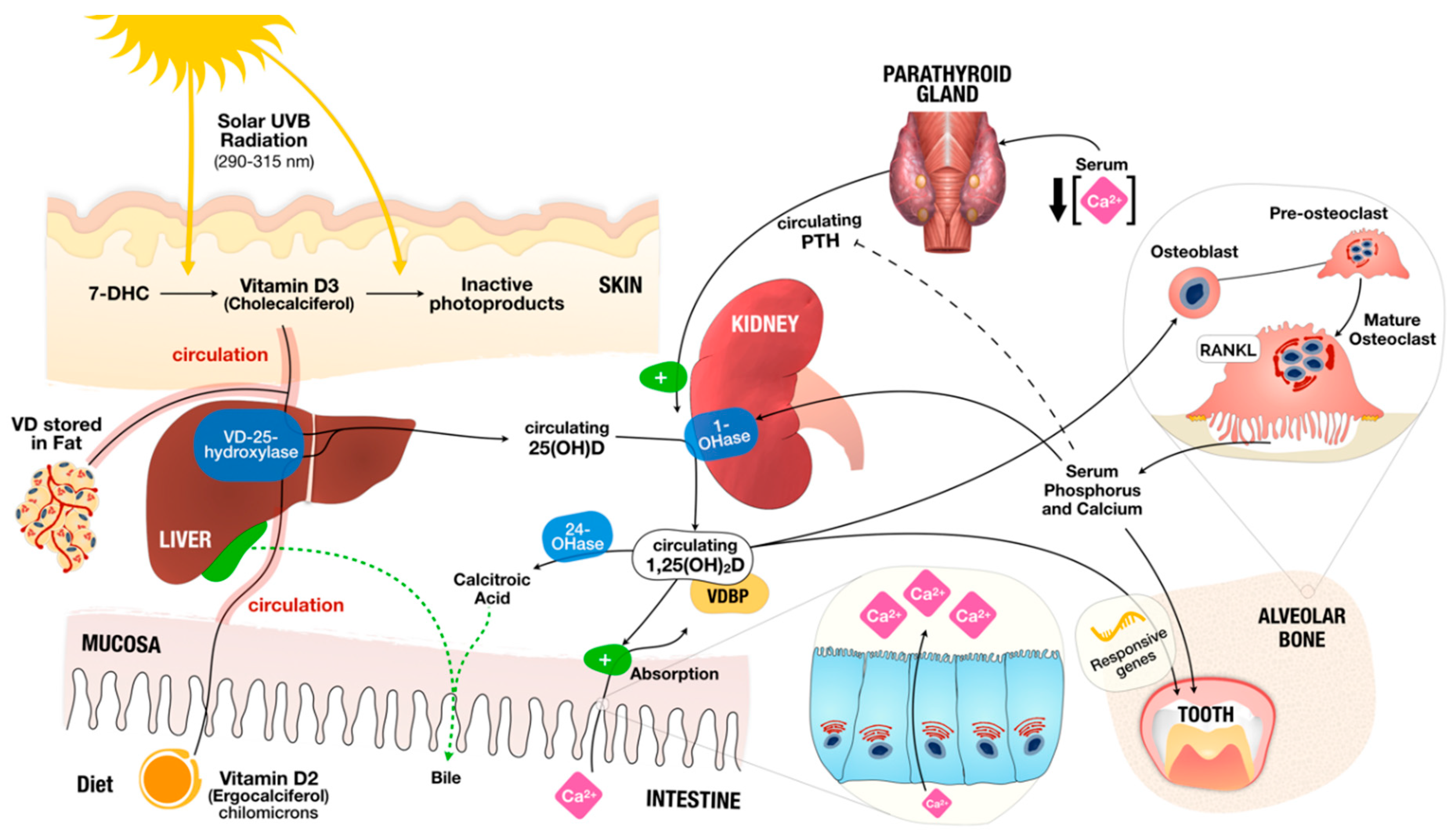
Nutrients Free Full Text Vitamin D Deficiency And Oral Health A Comprehensive Review Html
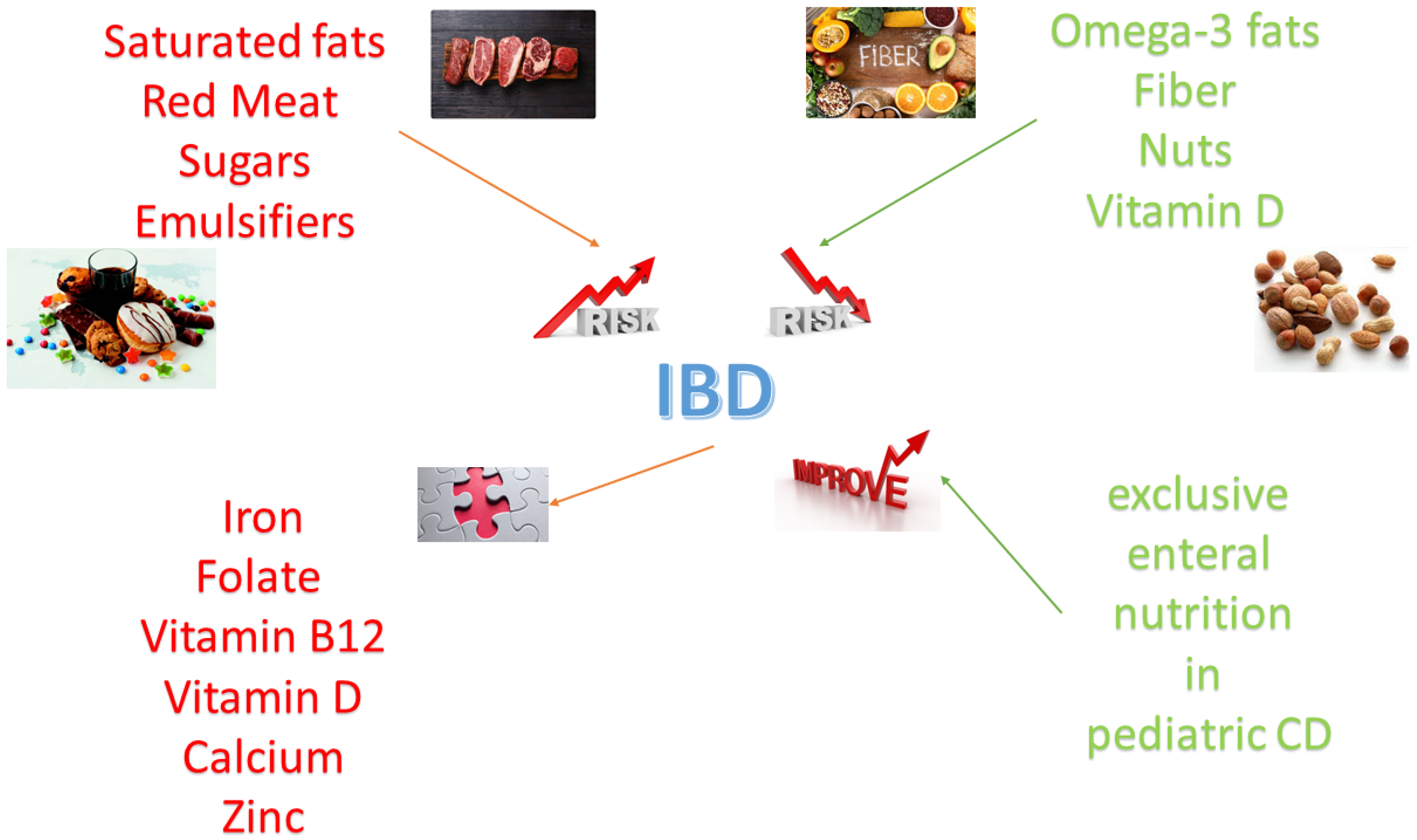
Nutrients Free Full Text Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Is There A Role For Nutritional Suggestions Html
/ibd-and-vitamin-d-levels-5087597-v1-b5a5c6143d02403a9da95c0c6f948012.jpg)
Post a Comment for "Review Article Vitamin D And Inflammatory Bowel Diseases"